
Manter a produção de louça sanitária cerâmica isenta de ferro
A louça sanitária é um termo frequentemente empregue na indústria cerâmica para descrever os aparelhos sanitários localizados em casas de banho e sanitas. A porcelana, um material cerâmico derivado do barro, é tradicionalmente utilizada para construir sanitas, cisternas, bidés, urinóis e lavatórios. Quando esmaltada, a porcelana é designada por "porcelana vítrea". Geralmente, é branca e pode ser chamada de louça sanitária de cerâmica, porcelana ou porcelana.

Atualmente, um número significativo de produtos sanitários é branco ou apresenta uma cor muito incolor. Isto leva à rejeição do produto afetado pela fábrica antes mesmo de ser libertado, uma vez que quaisquer defeitos são facilmente aparentes. Este é um processo demorado e dispendioso, uma vez que os materiais rejeitados são novamente descartados ou triturados e reintroduzidos no processo.
O ferro, seja sob a forma de ferro livre ou de um mineral que contenha ferro, é uma das causas mais comuns de defeitos. Após a queima, a contaminação por ferro resulta na formação de manchas negras desagradáveis e altamente visíveis na superfície do produto sanitário, ou cria uma fragilidade na estrutura cerâmica. Esta contaminação pode também afetar a cor do verniz, resultando na diminuição da sua luminosidade.
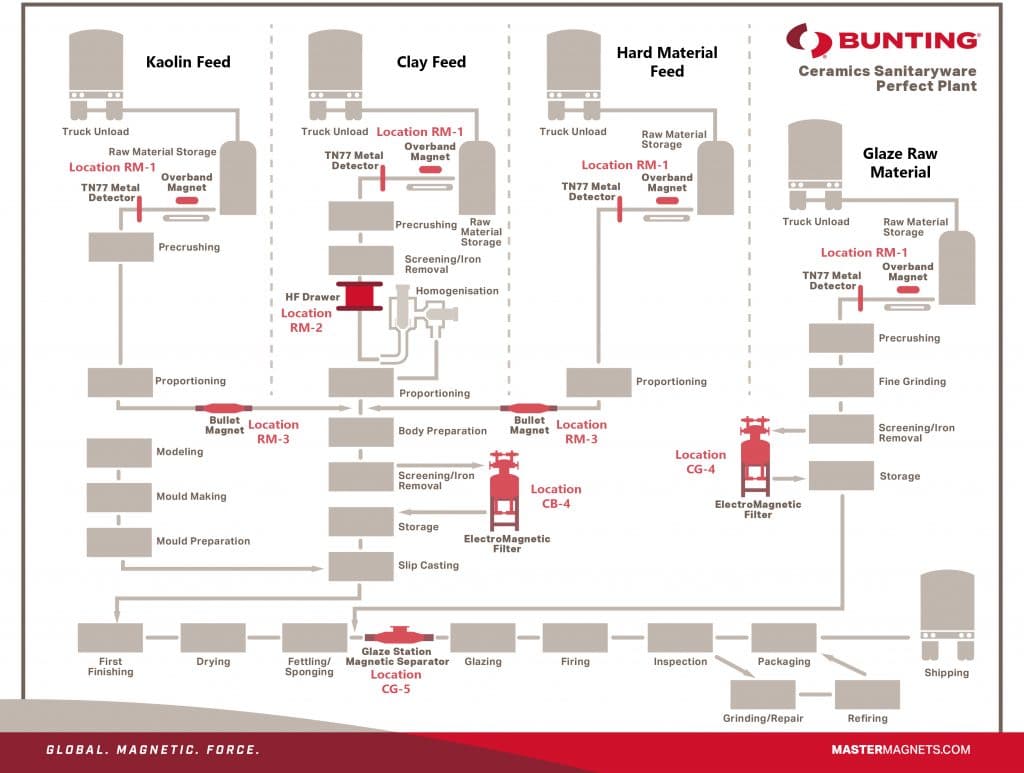
Uma planta típica de louça sanitária cerâmica que mostra localizações ideais para separadores magnéticos
Iron and Mineral-Iron Removal
The sanitaryware manufacturing process comprises numerous critical stages, such as:
Body preparation; Glaze preparation; Moulding and mould preparation; Casting; Drying; Control and spraying; Firing; Sorting; Refire/Rework;
To achieve the most effective separation of iron, mineral iron, and magnetic minerals, magnetic separators must be positioned and located in critical areas during this process.
Preparation of the Ceramic Body
The primary structure of the sanitaryware item is composed of a material mix known as the "Ceramic Body." The production of Ceramic Body involves the combination of basic materials, such as Kaolin, Feldspar, Silica, and Ball Clay. Ultimately, the completed fired sanitaryware is weakened by the presence of iron and mineral iron contamination in the ceramic body, which frequently results in cracking and fracture.

In the majority of instances, raw material suppliers have already eliminated a significant fraction, if not the entirety, of the larger free iron and stronger iron-bearing minerals. Nevertheless, tramp metal is frequently inadvertently introduced during the transportation and processing process. Tramp metal can result in substantial and expensive damage to processing equipment if it enters the pre-crushing stage or Ball Mill. Additionally, the tramp iron would be substantially reduced in size, which would result in its extensive dispersion throughout the body mix and an increasing difficulty in extracting it.
Before being batch-fed into the process, the unprocessed material is delivered and stored. The removal and detection of larger tramp metal, both ferrous and non-magnetic, are guaranteed by the combination of a Magnetic Separator and Metal Detector (RM-1) on the conveyor that feeds the raw material to the pre-crushing stage. Tramp iron is initially lifted and separated by a permanent Overband Magnet (or Suspended Plate Magnet) that is initially positioned over the input conveyor. This is succeeded by a TN77 Metal Detector, which is capable of detecting and removing non-magnetic metals, including manganese steel.
Technical Product Information: Overband Magnets Technical Product Information: TN77 Metal Detector
The removal of the vast majority of free fine iron and powerfully magnetic minerals, many of which have been liberated during the pre-crushing stage, is crucial before the kaolin, clay, and hard materials are mixed together to form the Ceramic Body.
A Drawer Filter Magnet (RM-2) is employed to separate fine iron and magnetic minerals that are released during crushing on the Clay feed line, following pre-crushing and screening. This magnet is equipped with high-strength Neodymium Tube Magnets.
HF Drawer Filter Magnet Technical Product Information
The capture of any liberated fine iron and powerfully magnetic minerals is guaranteed by locating a Bullet Magnet prior to mixing, following the pre-crushing and proportioning of the kaolin and the hard materials.
Technical Product Information: Bullet Magnets Separating Fine Magnetic Particles from Ceramic Body
The 'Ceramic Body' is subsequently formed by the combined and milled raw materials. The ceramic body is screened and subsequently subjected to a final stage of magnetic separation following the mixing process. This is the final opportunity to capture problematic magnetic particles, a task that is ideally adapted for a high-intensity Electro Magnetic Filter.

A magnetic stainless steel matrix is situated in the center of an electromagnetic coil in an electro magnetic filter. Approximately 10-12,000 gauss is the intensity of the magnetic field at the matrix's vertices. The Electro Magnetic Filter is used to circulate the ceramic body, which is then captured on the points of the matrix by very fine iron and weakly magnetic minerals.
The Electro Magnetic Filter undergoes an automatic cleansing sequence on a predetermined cycle, which is contingent upon the contamination level, in order to eliminate the magnetic particles that are captured.
Technological Product Information: Electro Magnetic Filter for Ceramic Sanitaryware Conservation Electro Magnetic Filter Iron-Free
The Ceramic Body is subsequently stored in preparation for slip casting after being cleansed.
Ceramic Glaze Preparation and Application
Ceramic glaze is a vitreous substance that has been fused to a ceramic body through firing, resulting in an impervious layer or coating. Throughout history, it has been employed to conceal and conceal iron-induced and other defects.
Zircon, feldspar, quartz, calcite, china clay, and zinc oxide are combined to create glaze. The ball mill is used to grind the basic material mixture.
Maintaining the Absence of Iron in Ceramic Sanitaryware
The Glaze's iron-free status is of greater importance than that of the Body. Any iron that is present in the Glaze will be visible on the surface of the sanitaryware product. The initial stage of separation, similar to that of Ceramic Body, concentrates on the raw material input. The risk of heavy contamination is mitigated by ensuring that the primary materials entering the process are free of tramp metal.
Once more, the optimal protection and separation are achieved prior to pre-crushing through the integration of a permanent Overband Magnet and TN77 Metal Detector (RM-1).
The Ceramic Glaze raw material blend is initially pre-crushed and subsequently finely ground prior to screening. The Glaze is subjected to a high-intensity electro magnetic filter following the sifting process. Arguably, this is the most critical magnetic separation stage in the entire sanitaryware facility, as it eliminates both fine iron and weakly magnetic minerals from the Glaze.
Once cleansed, the Ceramic Glaze is stored and transported to the glazing stations as required. The material undergoes a final Neodymium Magnetic Separator, such as a Liquid Pipeline Magnet or Magnetic Trap (CG-5), immediately before the glaze application. This captures any magnetic particles that have infiltrated the Glaze during storage or transportation to the glazing line.

As louças sanitárias esmaltadas são então colocadas num forno para queima e, em seguida, submetidas a um processo de inspeção para identificar quaisquer defeitos, como fissuras ou manchas, que possam estar presentes sob a forma de ferro ou outros materiais. Os produtos rejeitados serão retrabalhados ou triturados e reincorporados na matéria-prima.
Para evitar a reintrodução de produto contaminado no processo, as rejeições trituradas são passadas por um Separador Magnético de Tambor Permanente de Alta Intensidade ou por um Separador Magnético de Rolos de Terras Raras para remover o ferro.
Artigos Técnicos Relevantes:
Armazenamento de Louça Cerâmica com Ferro sem Manchas .
Preservação de Azulejos Cerâmicos sem Ferro.
Os resíduos são reduzidos através da separação magnética ideal.
O equipamento ideal para a separação magnética deve ser recomendado em conjunto com a compreensão do processo de fabrico de cerâmica. As operações de produção de cerâmica utilizam os separadores magnéticos mencionados nesta análise com sucesso. No entanto, cada processo de fabrico é distinto, e a visita de um Engenheiro de Vendas local da Bunting ajudará a compreender um processo específico e o problema da contaminação por ferro, bem como a propor uma solução específica.

A Beijing Sunlets Technology Co., Ltd. é líder global em fundição de alta pressão e automação industrial para cerâmica sanitária. Com mais de 18 anos de experiência, a Sunlets oferece soluções completas, incluindo design de fábrica, localização de fórmulas de barbotina e esmalte e apoio técnico em matéria-prima.
Com o apoio de mais de 200 patentes e um centro de investigação dedicado, a Sunlets garante soluções de produção inovadoras, eficientes e personalizadas para as principais marcas de louça sanitária de todo o mundo.
Para consulta gratuita de projeto e avaliação de solução de equipamento, contacte
Senhorita. Jenny SHEN/沈女士
jmshen0114@sunletsgroup.com
M/WeChat: +8618001297796